SKIN:Is the LARGEST ORGAN OF THE BODY. The skin and its DERIVATIVES which are:(hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) make up the INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. One of the main functions of the skin is PROTECTION.It protects the body from external factors such as BACTERIA, CHEMICALS, and TEMPERATURE.
LECTURES: Is INFORMATION,acquired through EDUCATION; the THEORETICAL or practical understanding of a special subject.
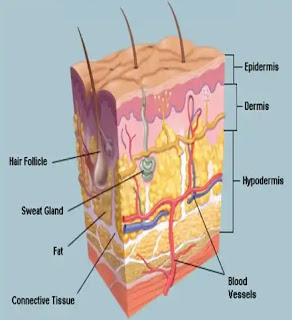
SKIN are divided into three(3) LAYERS/TISSUES:
Which are;
* EPIDERMIS-These is the SURFACE meaning the TOP LAYER of the skin,these is skin that you can see and touch. KERATIN, a protein inside skin cells, makes up the skin cells and, along with other proteins, sticks together to form this layer. The epidermis:
I. ACTS AS A PROTECTIVE BARRIER: The epidermis keeps bacteria and germs from entering your body and bloodstream and causing infections. It also protects against rain, sun and other elements.
II. MAKES NEW SKIN: The epidermis continually makes new skin cells. These new cells replace the approximately 40,000 old skin cells that your body sheds every day. YOU HAVE NEW SKIN EVERY 30 DAYS.
III. PROTECT YOUR BODY: Langerhans cells in the epidermis are part of the body’s IMMUNE SYSTEM. They help fight off germs and infections.
IV. PROVIDES SKIN COLOR: The epidermis contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. The amount of MELANIN you have determines the color of your skin, hair and eyes. People who make more MELANIN have darker skin and may tan more quickly.
* DERMIS-These is the MIDDLE LAYER of the skin that makes up 90% of skin’s thickness:This DERMIS layer of skin has;
I. HAS COLLAGEN AND ELASTIN: Collagen is a protein that makes skin cells strong and resilient. Another protein found in the dermis, elastin, keeps skin flexible. It also helps stretched skin regain its shape.
II. GROWS HAIR: The roots of hair follicles attach to the dermis.
III. KEEPS YOU IN TOUCH: Nerves in the dermis tell you when something is too hot to touch, itchy or super soft. These nerve receptors also help you feel pain.
IV. MAKES OIL: Oil glands in the dermis help keep the skin soft and smooth. Oil also prevents your skin from absorbing too much water when you swim or get caught in a rainstorm.
V. Produces sweat: Sweat glands in the dermis release sweat through skin pores. Sweat helps regulate your body temperature.
VI. Supplies blood: Blood vessels in the dermis provide nutrients to the epidermis, keeping the skin layers healthy.
* HYPODERMIS-These is the 3rd LAYER of the skin can also be said as the BOTTOM LAYER (FATTY LAYER)
The HYPODERMIS:
I. CUSHIONS MUSCLES AND BONES: Fat in the hypodermis protects muscles and bones from injuries when you fall or are in an accident.
II. HAS CONNECTIVE TISSUE: This tissue connects layers of skin to muscles and bones.
III. HELPS THE NERVES AND BLOOD VESSELS: Nerves and blood vessels in the dermis (middle layer) get larger in the hypodermis. These nerves and blood vessels branch out to connect the hypodermis to the rest of the body.
IV. REGULATES BODY TEMPERATURE: Fat in the hypodermis keeps you from getting too cold or hot.
NOTES:One inch of your skin has approximately 19 million skin cells and 60,000 melanocytes (cells that make melanin or skin pigment). It also contains 1,000 nerve endings and 20 blood vessels.
CONDITIONS THAT AFFECT THE SKIN:
As the body’s external protection system, your skin is at risk for various problems.
These include:
I. Allergies like contact dermatitis and poison ivy rashes.
II. Blisters.
III. Bug bites, such as spider bites, tick bites and mosquito bites.
IV. Skin cancer, including melanoma.
V. Skin infections like cellulitis.
VI. Skin rashes and dry skin.
VII. Skin disorders like acne, eczema, psoriasis and vitiligo.
VIII. Skin lesions, such as moles, freckles and skin tags.
IX. Wounds, burns (including sunburns) and scars
You lose collagen and elastin as you age increases.This causes the skin’s middle layer (dermis) to get thinner. As a result, the skin may sag and develop wrinkles.
While you can’t stop the aging process, these actions can help maintain healthier skin:
I. Apply sunscreen every day (even if you’re mostly indoors). Choose a sunscreen with a broad-spectrum sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30.
II. Don’t tan indoors or outdoors. Tanning skin damage. It ages skin and can cause skin cancer.
III. Find healthy ways to manage stress. Stress can make certain skin conditions worse.
IV. Perform regular skin and mole checks to look for changes that may be signs of skin cancer.
V. QUIT SMOKING AND USING TOBACCO PRODUCTS. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarette and electronic cigarette changes skin faster.
VI. Use gentle cleansers to wash your face in the morning and at night.
VII. Shower regularly and apply moisturizing lotion to prevent dry skin.
WHEN SHOULD I TALK TO MY DOCTOR?
When you have SYMPTOMS like:
- Change in size, color, shape or symmetry of a mole.
- Skin changes like a new mole.
- A cut that a household bandage can’t close (that may need stitches).
- Severe, blistering burns.
- Signs of skin infections like red streaks or yellow discharge.
- Unexplained skin rash or skin condition.



0 Comments